What is HL7 Interface?
The HL7 Interface, or Health Level Seven Interface, is a globally recognized set of standards designed to facilitate the seamless exchange of healthcare data between disparate systems. These standards enable healthcare organizations to transmit patient information, laboratory results, billing details, and other vital data securely and efficiently. By standardizing the way data is formatted and shared, HL7 interfaces ensure that diverse healthcare systems—such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), and Radiology Information Systems (RIS)—can communicate effectively without manual intervention.
The importance of the HL7 Interface lies in its ability to foster interoperability across healthcare platforms. In an era where patient care often involves multiple providers and institutions, ensuring that accurate, up-to-date information is readily available is crucial. By enabling data uniformity and real-time information exchange, HL7 interfaces not only enhance clinical decision-making but also streamline workflows, reduce administrative burdens, and improve patient outcomes. For organizations aiming to achieve true digital transformation in healthcare, implementing HL7 standards is an essential step.
Components of an HL7 Interface
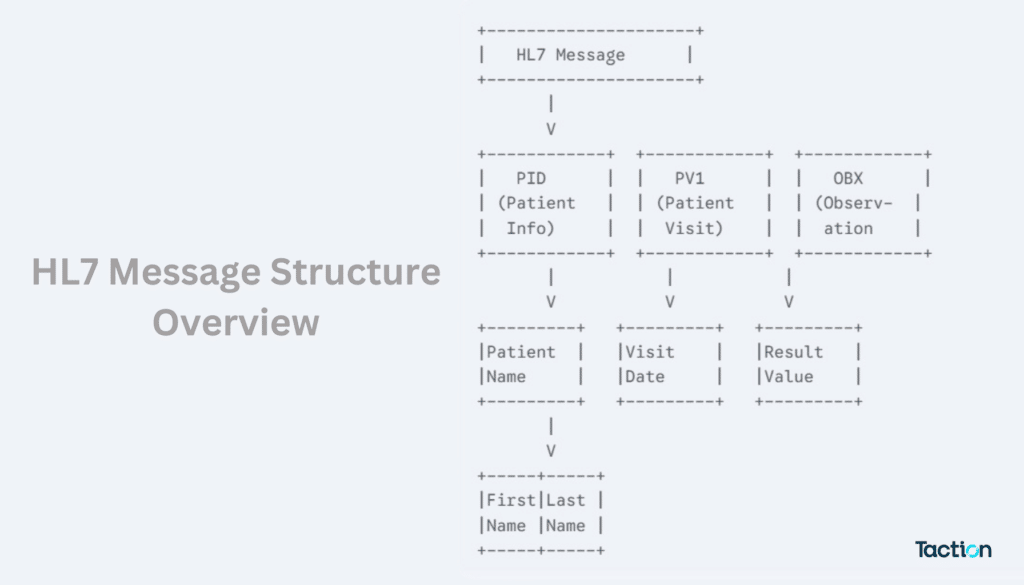
1. Messages: The Foundation of Data Exchange
Messages form the highest level of abstraction within the HL7 framework. Each message is a structured communication unit designed to carry specific types of healthcare information, such as patient admissions, lab results, or billing transactions. These messages serve as the medium through which healthcare systems exchange data, ensuring a standardized flow of information that is both secure and accurate.
2. Segments: The Building Blocks of Messages
Within each message are segments, which group related data elements into logical categories. Segments define the type of information being transmitted, such as patient identification (PID), lab results (OBX), or visit details (PV1). Each segment is uniquely identified by a three-character code, making it easy to interpret and implement across various healthcare systems. Segments provide a clear framework for organizing data into manageable units.
3. Fields: The Data Containers
Segments are further composed of fields, which hold the actual data being exchanged. For example, the PID segment contains fields for patient name, date of birth, and medical record number. Fields can be broken down into components and sub-components to provide even more detailed and granular information. This hierarchical organization allows for precise and accurate data exchange, critical for effective healthcare communication.
By structuring data in layers—messages, segments, and fields—HL7 interfaces ensure that healthcare systems can efficiently interpret and share complex information, enabling seamless interoperability and improved patient care.
Evolution of HL7 Standards
1. HL7v2: The Pioneer in Healthcare Data Exchange
HL7 Version 2 (HL7v2) is the most widely adopted standard in healthcare interoperability, serving as the cornerstone for healthcare data exchange since its introduction in the late 1980s. Its straightforward, delimited messaging format allows healthcare systems to share patient information, laboratory results, and other critical data efficiently. HL7v2 is highly flexible, supporting a wide range of use cases, from simple data exchanges to complex workflows. This adaptability has made HL7v2 the backbone of healthcare communication, used extensively in hospitals, laboratories, and clinics worldwide. Despite the emergence of newer standards, HL7v2 remains foundational due to its extensive implementation and reliability.
2. HL7v3: XML-Based Messaging for Enhanced Data Structuring
HL7 Version 3 (HL7v3) represents a significant evolution, introducing a more structured and rigorous framework for data exchange. Unlike HL7v2’s delimited format, HL7v3 uses an XML-based messaging standard, offering greater precision and standardization. This approach ensures that clinical and administrative data are exchanged in a consistent and unambiguous manner. However, due to its complexity and steep learning curve, HL7v3 has seen limited adoption compared to its predecessor. It remains valuable for specialized applications, especially in systems requiring a high degree of data integrity and detailed structuring.
3. FHIR: The Future of Healthcare Interoperability
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is the latest innovation in HL7 standards, designed to address the challenges of modern healthcare systems. FHIR combines the best features of HL7v2 and HL7v3, offering a flexible, resource-based approach to data exchange. It uses RESTful APIs, making it ideal for integration with web and mobile applications. FHIR simplifies interoperability by providing discrete, reusable resources that can be combined to address a wide range of use cases, from EHR integration to patient data sharing. Its compatibility with emerging technologies positions FHIR as the standard of choice for the future of healthcare interoperability.
This progression from HL7v2 to FHIR highlights the ongoing evolution of healthcare standards, driven by the need for greater efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility in data exchange.
Benefits of Implementing HL7 Interfaces

1. Improved Data Uniformity and Interoperability
HL7 interfaces play a pivotal role in achieving data uniformity and seamless interoperability across healthcare systems. By providing standardized data formats, HL7 eliminates discrepancies in how information is recorded and shared between systems such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), and Radiology Information Systems (RIS). This standardization ensures that all healthcare providers access consistent, up-to-date patient information, reducing the risk of errors in clinical decision-making. Additionally, HL7’s ability to integrate diverse systems eliminates the need for redundant data entry, minimizing duplication and maintaining the integrity of healthcare data.
2. Enhanced Workflow Automation
One of the most significant advantages of HL7 interfaces is the automation of healthcare workflows. By enabling systems to communicate without human intervention, HL7 reduces the need for manual data entry and repetitive administrative tasks. For example, when a lab result is generated, it is automatically sent to the appropriate clinician’s EHR system, eliminating delays and manual transcription errors. This automation not only accelerates data transfer but also frees up valuable time for healthcare staff, allowing them to focus on patient care. Improved efficiency in workflows leads to faster diagnosis and treatment, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of care.
3. Streamlined Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare organizations must adhere to strict regulatory requirements, including those related to data security, privacy, and reporting. HL7 interfaces simplify compliance by enabling seamless electronic data sharing with regulatory bodies. For instance, HL7 facilitates the automatic reporting of patient data for public health surveillance or quality improvement programs, ensuring timely and accurate submissions. Moreover, the standard’s emphasis on data integrity and security helps organizations meet regulations such as HIPAA, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
By implementing HL7 interfaces, healthcare organizations can not only achieve interoperability and efficiency but also meet regulatory demands with ease, ensuring a more streamlined and secure healthcare ecosystem.
Challenges in HL7 Integration and Solutions
1. Compatibility Issues
One of the primary challenges in HL7 integration is ensuring compatibility between different healthcare systems. Since healthcare providers often use diverse systems for EHRs, lab management, billing, and other functions, integrating them seamlessly can be complex. Legacy systems may lack support for newer HL7 standards, while modern systems may not fully accommodate older ones like HL7v2. This discrepancy can lead to data inconsistencies, communication failures, or incomplete data transfers, potentially impacting patient care. Addressing compatibility issues requires customized solutions, such as tailored middleware or adapters, to bridge the gaps between disparate systems.
2. Security Concerns
Data security is a critical concern in HL7 integration, given the sensitive nature of healthcare information. HL7 messages often include patient details, medical histories, and billing data, making them a target for cyberattacks. Without robust security measures, data breaches could result in significant financial and reputational damage, as well as violations of regulations like HIPAA. Ensuring secure data exchange requires strong encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits to protect patient information and maintain compliance with industry standards.
3. Solutions
To overcome these challenges, engaging HL7 integration experts is essential. These professionals have in-depth knowledge of HL7 standards and can design customized solutions to address compatibility issues and enhance security. They can implement robust integration frameworks, configure middleware, and ensure that all systems communicate effectively. Additionally, experts can establish secure data transfer protocols, conduct compliance checks, and offer ongoing support to adapt to evolving needs. With the right expertise, healthcare organizations can navigate HL7 integration challenges smoothly, ensuring seamless interoperability and secure, efficient data exchange.
By addressing these challenges proactively, healthcare providers can fully leverage the benefits of HL7, enabling better patient care and operational efficiency.
Future Trends in HL7 and Healthcare Interoperability
1. Advancements in FHIR
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is rapidly gaining traction as the future of healthcare interoperability. Designed to address the limitations of previous HL7 standards, FHIR provides a modern, resource-based framework that is highly flexible and developer-friendly. Its ability to use RESTful APIs makes it ideal for integration with web and mobile applications, offering real-time access to healthcare data. FHIR’s modular structure allows healthcare providers to exchange only the necessary data, reducing complexity and improving efficiency. With its compatibility across various systems and applications, FHIR is set to drive significant advancements in care coordination, patient engagement, and telehealth services, positioning it as a cornerstone of digital healthcare transformation.
2. Integration with Emerging Technologies
The future of HL7 standards lies in their convergence with emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain. AI, when integrated with HL7 data, can enhance predictive analytics, clinical decision support, and personalized medicine by analyzing large volumes of structured healthcare information. Blockchain, on the other hand, offers a secure and transparent way to manage and share healthcare data. By leveraging blockchain’s decentralized nature, HL7 standards can ensure tamper-proof data exchange while maintaining patient privacy and regulatory compliance. Additionally, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with HL7 can enable real-time monitoring and data sharing, further enhancing patient care.
These trends signify a shift towards a more connected, secure, and intelligent healthcare ecosystem, where HL7 standards will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare interoperability.
| Feature | HL7 v2 | HL7 v3 | FHIR |
| Data Format | Delimited text | XML | XML, JSON |
| Flexibility | Low | Moderate | High |
| Implementation | Simple | Complex | Relatively Simple |
| Learning Curve | Low | High | Moderate |
| Use Cases | – Hospital Info Systems <br> – Lab Systems | – Clinical Documents <br> – Public Health Reporting | – Mobile Health Apps <br> – EHR Data Exchange <br> – Clinical Research |
| Maturity | Widely adopted | Mature, but less used | Growing rapidly |
| Interoperability | Limited | Good | Excellent |
Conclusion
HL7 interfaces have revolutionized the way healthcare data is exchanged, driving seamless interoperability across diverse systems. By standardizing communication between EHRs, laboratories, billing systems, and other healthcare platforms, HL7 ensures that critical patient information is always accessible, accurate, and up-to-date. This not only improves clinical decision-making but also enhances workflow efficiency, reduces administrative burdens, and streamlines regulatory compliance. From the foundational HL7v2 standard to the innovative FHIR framework, these interfaces are pivotal in building a connected healthcare ecosystem that delivers better patient outcomes and operational excellence.
For healthcare organizations looking to optimize their data exchange processes, partnering with a trusted expert is crucial. At Taction Software, we offer customized HL7 integration solutions tailored to meet your unique needs. Whether you’re implementing FHIR, addressing compatibility issues, or ensuring data security, our team of seasoned professionals ensures a smooth, efficient, and secure integration process. Reach out to Taction Software today to elevate your healthcare interoperability and deliver exceptional care with confidence.